SAND-Reasoning: Best-in-class Large Reasoning Model Built with Synthetic Data only using AMD GPUs
Model Summary
We introduce SAND-Math-Qwen2.5-32B and SAND-MathScience-DeepSeek-Qwen32B, reasoning models built entirely using a synthetic data pipeline running on the AMD ROCm™ stack and AMD Instinct™ MI325 GPUs.
By prioritizing data difficulty along with quantity, we demonstrate that high-difficulty synthetic data can elevate prior-generation models to match or exceed modern proprietary models. SAND-Math-Qwen2.5-32B is fine-tuned from Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct on just 14k synthetic math samples, achieving strong reasoning capabilities with minimal data outperforming other data distillation and post training approaches. SAND-MathScience-DeepSeek-Qwen32B is fine-tuned from DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B on a compact dataset of 27k samples (15k Math + 12k Science), achieving a generational leap in performance that rivals Qwen3-32B.
We are releasing the models, datasets, and code to empower the community to build their own state-of-the-art reasoning models using AMD hardware.
📊 Benchmark Results
We conducted extensive experiments to validate that our pipeline yields superior results compared to models trained on significantly larger datasets.
1. Bridging the Generational Gap
Fine-tuning the Qwen2.5-based DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B on our mixed Math/Science dataset allows it to rival and even surpass the next-generation Qwen3-32B on key benchmarks.
| Model | AIME24 | AIME25 | MATH500 | GPQA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek-Distilled-Qwen32B (Base) | 72.6 | 54.9 | 94.3 | 62.1 |
| EXAONE Deep 32B | 72.1 | 65.8 | 95.8 | 66.1 |
| Qwen3-32B (Thinking mode) | 81.4 | 72.9 | 97.0 | 68.4 |
| SAND-MathScience-DeepSeek-Qwen32B (Ours) | 83.85 | 78.33 | 93.85 | 68.72 |
2. Efficiency: Unlocking Reasoning with Less Data
Using only 14k synthetic math samples and standard SFT (no RL), our approach outperforms models trained on datasets 5x to 50x larger.
| Model | Data Size | AIME24 | AIME25 | MATH500 | GPQA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct (Base) | - | 16.7 | 13.3 | 83.4 | 53.5 |
| DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B | 800k | 72.6 | 54.9 | 94.3 | 62.1 |
| Light-R1-32B | 79k | 73.0 | 64.3 | 93.3 | 60.6 |
| OpenThinker-32B | 114k | 66.0 | 53.3 | 89.4 | 57.6 |
| SAND-Math-Qwen2.5-32B (Ours) | 14k | 74.01 | 68.18 | 92.05 | 60.8 |
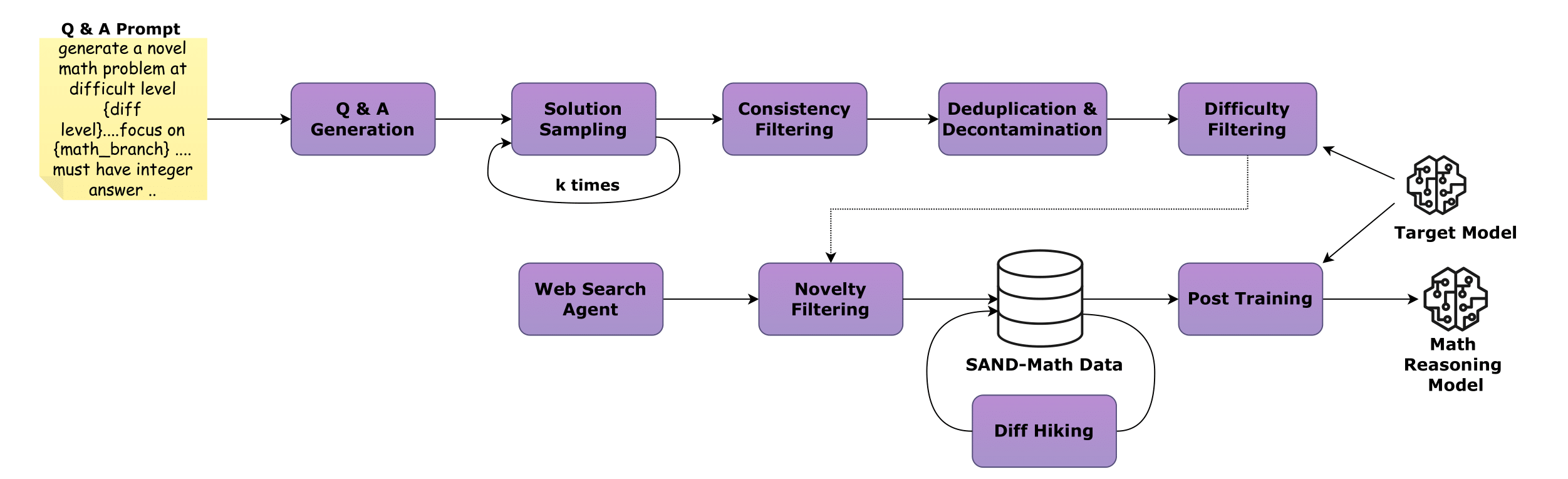
⚙️ The Synthetic Data Pipeline
Our results are powered by a 4-stage automated pipeline running on AMD hardware that prioritizes difficulty and novelty over volume. Unlike datasets that recycle easy problems, our pipeline leverages a Teacher Model (GPT-OSS120b) to generate, validate, and systematically "hike" the difficulty of reasoning problems.
Pipeline Stages
Stage 1: QA Generation & Consistency 🛠️
- Generates novel problems from scratch
- Enforces correctness by requiring the teacher to generate multiple independent solution paths
- Only questions where all answers align are kept
Stage 2: De-duplication & Decontamination 🧹
- Removes internal duplicates via embedding similarity
- Crucial Step: Scans against known test sets (AIME, MATH, GPQA) to ensure zero contamination
Stage 3: Difficulty Hiking 🏔️
- Moderately challenging questions are rewritten by the teacher model
- Introduces deeper reasoning chains, added constraints, or cross-domain logic
- Systematically elevates complexity
- Configurable step primarily used when initial generation yields insufficient volume of high-difficulty samples
🚀 Quick Start
Python Inference (Transformers)
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "amd/SAND-Math-Qwen2.5-32B"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype="auto",
device_map="auto"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
# Example prompt
prompt = "Find the number of pairs of positive integers $(m, n)$ such that $m^2 + n < 22$ and $n^2 + m < 22$."
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=4096,
temperature=0.7, # Recommended temperature
do_sample=True
)
generated_ids = [
output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(model_inputs.input_ids, generated_ids)
]
response = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
print("Response:", response)
Serving (vLLM & SGLang)
You can easily serve this model as an OpenAI-compatible API endpoint.
Using SGLang:
python -m sglang.launch_server --model-path amd/SAND-Math-Qwen2.5-32B --max-model-len 32768
Using vLLM:
vllm serve amd/SAND-Math-Qwen2.5-32B --max-model-len 32768
💡 Usage Recommendations
To replicate our performance benchmarks and achieve the best reasoning results, we strongly recommend the following configurations:
- Temperature: Set
temperature=0.7. DO NOT use greedy decoding, as it can lead to performance degradation and repetitive loops. - Prompting: For mathematical problems, include a directive to enforce structure:
"Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \boxed{}."
- Context Length: We recommend allowing an output length of 32,768 tokens. This ensures the model has sufficient space for long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) generation.
- Thinking Token: It is recommended to enforce the model to initiate its response with the
<think>\ntoken to trigger the reasoning mode effectively. - Evaluation: When benchmarking, conduct multiple passes (Pass@K) and average the results for stability.
📜 License
This project is licensed under the Open RAIL-MSD license. This is an open, royalty-free license that permits commercial use, modification, and distribution of the dataset, models, and source code.
The license includes standard use-based restrictions to prevent harmful applications (e.g., illegal activities, generating harmful content, high-risk applications). These restrictions are designed to promote responsible AI development while keeping the license permissive for legitimate use cases.
For full license terms and conditions, please see the LICENSE file.
Citation
If you use this model, dataset, or pipeline in your research, please cite our work:
@misc{manem025sandmathusingllmsgenerate,
title={SAND-Math: Using LLMs to Generate Novel, Difficult and Useful Mathematics Questions and Answers},
author={Chaitanya Manem and Pratik Prabhanjan Brahma and Prakamya Mishra and Zicheng Liu and Emad Barsoum},
year={2025},
eprint={2507.20527},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.20527},
}
- Downloads last month
- -