Datasets:
task_categories:
- text-retrieval
tags:
- text2sql
- text-2-sql
- texttosql
- text-to-sql
license: cc-by-nc-4.0
language:
- en
pretty_name: FINCH
size_categories:
- 10K<n<100K
Dataset Card for FINCH - Financial Intelligence using Natural language for Contextualized SQL Handling
A comprehensive collection of SQLite databases from the FINCH benchmark, containing 33 databases with 292 tables and 75,725 natural language-SQL pairs across diverse financial domains for Text-to-SQL research and development.
Dataset Details
Dataset Description
Curated by: Domyn
Authors: Avinash Kumar Singh, Bhaskarjit Sarmah, Stefano Pasquali
Language(s): English
License: CC-BY-NC-4.0
FINCH (Financial Intelligence using Natural language for Contextualized SQL Handling) provides SQLite database files from a carefully curated financial Text-to-SQL benchmark that consolidates and extends existing resources into a unified, finance-specific dataset. Each database preserves original schema structure, relationships, and data while focusing specifically on financial domains and applications.
This dataset addresses a critical gap in Text-to-SQL research: despite significant progress in general-domain benchmarks, financial applications remain especially challenging due to complex schemas, domain-specific terminology, and high stakes of error. FINCH provides the first large-scale, finance-oriented Text-to-SQL benchmark suitable for both evaluation and fine-tuning.
Dataset Sources
Paper: FINCH: Financial Intelligence using Natural language for Contextualized SQL Handling (coming soon)
Key Features
- 33 SQLite databases specifically curated for financial applications
- 292 tables with 2,233 columns and 177 relations
- 75,725 NL-SQL pairs for comprehensive training and evaluation
- Financial domain focus including retail, banking, insurance, e-commerce, funds, stocks, and accounting
- Direct SQLite format - ready for SQL queries and analysis
- Preserved relationships - foreign keys and indexes intact
- Multi-difficulty coverage with easy, medium, and hard query complexity levels
Dataset Structure
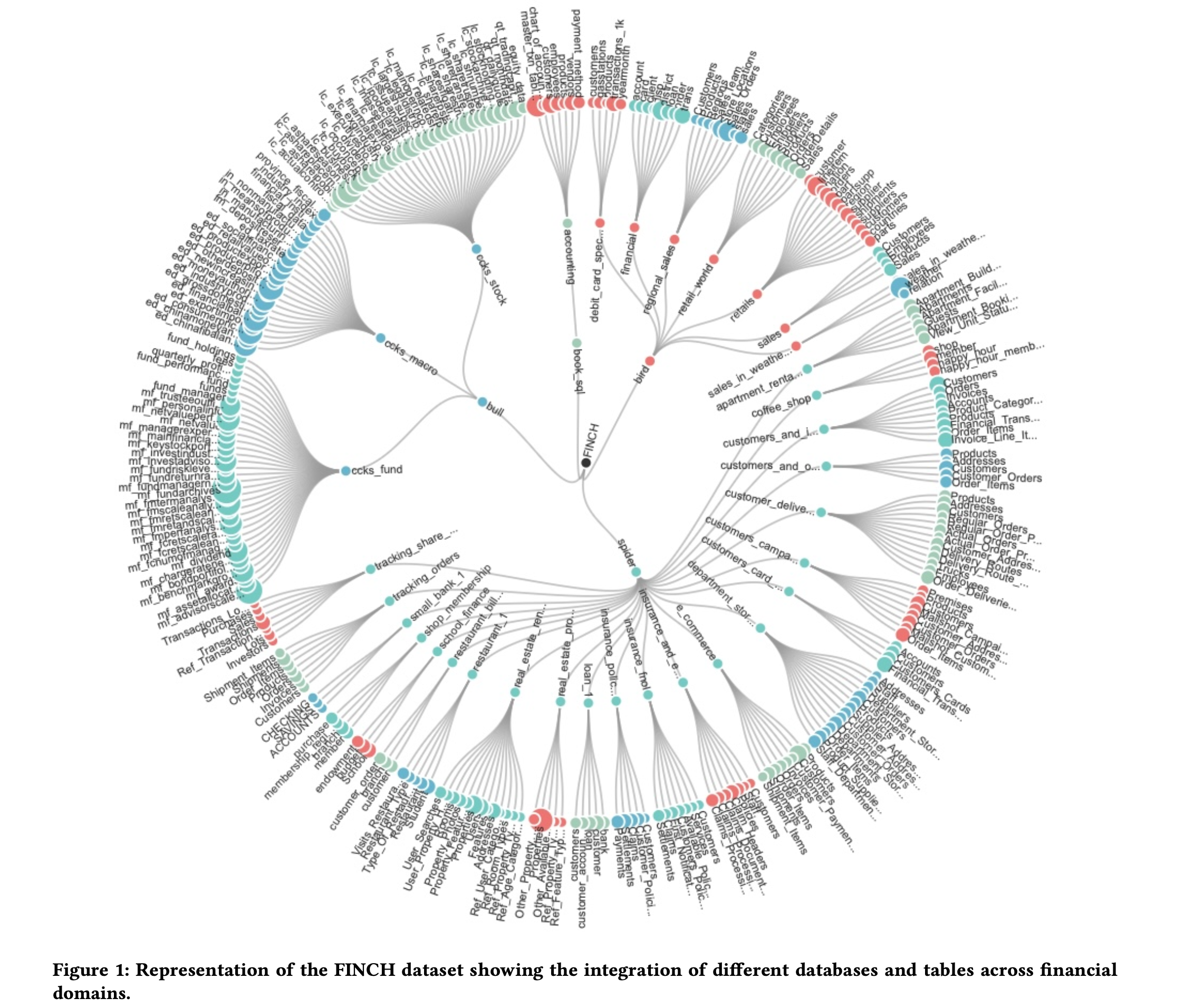
The dataset is organized by financial domain with meaningful database names:
File Organization
finch/
├── spider/ # 22 SQLite files (financial subset from Spider)
├── bird/ # 7 SQLite files (financial subset from BIRD)
├── bull/ # 3 SQLite files (BULL/CCKS financial data)
└── book_sql/ # 1 SQLite file (BookSQL accounting data)
Financial Domains Covered
Retail & E-commerce
- customers_and_invoices: E-commerce customer and billing systems
- e_commerce: Online retail transactions and order management
- department_store: Retail chain operations and inventory management
- shop_membership: Customer loyalty and membership programs
Banking & Financial Services
- financial: Czech bank transactions and loan portfolios (1M+ records)
- small_bank: Banking account management systems
- loan_1: Loan processing and customer account data
Insurance & Risk Management
- insurance_policies: Insurance claims and policy management
- insurance_and_eClaims: Electronic claims processing systems
- insurance_fnol: First notification of loss handling
Investment & Trading
- ccks_fund: Mutual fund management and performance data
- ccks_stock: Stock market data and trading information
- tracking_share_transactions: Investment portfolio tracking
Sales & Marketing
- sales: Large-scale sales transactions (6M+ records)
- sales_in_weather: Sales data correlated with external factors
- customers_campaigns_ecommerce: Marketing campaign effectiveness
Accounting & Financial Reporting
- accounting: Complete accounting system with 185+ tables covering transactions, customers, vendors, and financial reporting
- school_finance: Educational institution financial management
Dataset Format & Examples
Data Files Structure
finch_dataset.json: Main dataset file with 75,725 NL-SQL pairs (appears in HF dataset viewer)schemas/database_schemas.yaml: Database schema metadata for all 33 databases (auxiliary file)text2sql-db/: SQLite database files organized by source (auxiliary files)
Sample Data from finch_dataset.json
[
{
"question_id": 1,
"db_id": "financial",
"db_name": "bird",
"question": "How many accounts who choose issuance after transaction are staying in East Bohemia region?",
"partition": "dev",
"difficulty": "medium",
"SQL": "SELECT COUNT(t2.account_id) FROM district AS t1 INNER JOIN account AS t2 ON t1.district_id = t2.district_id WHERE t1.a3 = 'east bohemia' AND t2.frequency = 'poplatek po obratu'"
},
{
"question_id": 2,
"db_id": "financial",
"db_name": "bird",
"question": "How many accounts who have region in Prague are eligible for loans?",
"partition": "dev",
"difficulty": "easy",
"SQL": "SELECT COUNT(t1.account_id) FROM account AS t1 INNER JOIN loan AS t2 ON t1.account_id = t2.account_id INNER JOIN district AS t3 ON t1.district_id = t3.district_id WHERE t3.a3 = 'prague'"
},
{
"question_id": 3,
"db_id": "financial",
"db_name": "bird",
"question": "The average unemployment ratio of 1995 and 1996, which one has higher percentage?",
"partition": "dev",
"difficulty": "easy",
"SQL": "SELECT DISTINCT IIF(AVG(a13) > AVG(a12), '1996', '1995') FROM district"
}
]
Schema Information (schemas/database_schemas.yaml)
The schemas/database_schemas.yaml file contains comprehensive schema metadata for all databases:
financial:
db_id: financial
table_names_original:
- account
- card
- client
- disp
- district
- loan
- order
- trans
table_names:
- account
- card
- client
- disposition
- district
- loan
- order
- transaction
column_names_original:
- [-1, "*"]
- [0, "account_id"]
- [0, "district_id"]
- [0, "frequency"]
- [0, "date"]
column_types:
- text
- number
- number
- text
- text
foreign_keys:
- [2, 1]
- [4, 2]
primary_keys:
- 1
Example Usage
Loading with Python
Primary Method: Using datasets library (Recommended)
from datasets import load_dataset
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
import sqlite3
import yaml
# Load the main dataset using HuggingFace datasets library
dataset = load_dataset("domyn/FINCH")
print(f"Dataset: {dataset}")
print(f"Number of examples: {len(dataset['train'])}")
# Access individual examples
sample = dataset['train'][0]
print(f"Question: {sample['question']}")
print(f"SQL: {sample['SQL']}")
print(f"Database: {sample['db_id']}")
print(f"Difficulty: {sample['difficulty']}")
# Load schema information for the database
schema_path = hf_hub_download(repo_id="domyn/FINCH", filename="schemas/database_schemas.yaml")
with open(schema_path, 'r') as f:
schemas = yaml.safe_load(f)
# Download the corresponding SQLite database
db_path = hf_hub_download(
repo_id="domyn/FINCH",
filename=f"text2sql-db/text2sql/bird/{sample['db_id']}.sqlite"
)
# Execute the SQL query on the actual database
conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path)
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(sample['SQL'])
results = cursor.fetchall()
print(f"Query Results: {results}")
Alternative Method: Direct file download
import json
import sqlite3
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
# Alternative: Load dataset JSON file directly
samples_path = hf_hub_download(repo_id="domyn/FINCH", filename="finch_dataset.json")
with open(samples_path, 'r') as f:
dataset = json.load(f)
sample = dataset[0] # First sample
print(f"Question: {sample['question']}")
print(f"SQL: {sample['SQL']}")
Financial Query Examples
# Analyze banking transactions
cursor.execute("""
SELECT account_id, SUM(amount) as total_balance
FROM transactions
WHERE transaction_date >= '2023-01-01'
GROUP BY account_id
ORDER BY total_balance DESC
""")
# Insurance claims analysis
cursor.execute("""
SELECT policy_type, COUNT(*) as claim_count, AVG(claim_amount)
FROM claims c
JOIN policies p ON c.policy_id = p.policy_id
WHERE claim_status = 'approved'
GROUP BY policy_type
""")
Schema Exploration
# Get all tables
cursor.execute("SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type='table'")
tables = cursor.fetchall()
print("Available tables:", tables)
# Get detailed schema information
cursor.execute("PRAGMA table_info(transactions)")
schema = cursor.fetchall()
for column in schema:
print(f"Column: {column[1]}, Type: {column[2]}")
Data Quality & Statistics
Database Statistics
📊 TOTAL DATABASES: 33
📅 FINANCIAL DOMAINS: 8+ specialized areas
🏢 TABLES: 292 across all databases
🔗 RELATIONS: 177 foreign key relationships
💼 NL-SQL PAIRS: 75,725 total examples
| Source | Database Count | Table Count | NL-SQL Pairs | Domain Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spider (financial) | 22 | 145 | 1,100 | Cross-domain financial |
| BIRD (financial) | 7 | 48 | 1,139 | Large-scale realistic |
| BULL/CCKS | 3 | 99 | 4,966 | Chinese financial markets |
| BookSQL | 1 | 185 | 68,907 | Accounting systems |
| TOTAL | 33 | 292 | 75,725 | Financial |
Difficulty Distribution
- Easy queries: 9,358 examples (12.4%)
- Medium queries: 33,780 examples (44.6%)
- Hard queries: 32,587 examples (43.0%)
Quality Assurance
The dataset has undergone extensive validation and cleaning:
- ✅ SQL execution verified for all 75,725 queries
- ✅ Schema consistency maintained across all databases
- ✅ Error correction performed on original datasets:
- BIRD: 327 queries fixed (column names, table references)
- BULL: 60 queries corrected (syntax errors, invalid references)
- BookSQL: 9,526 queries repaired (column names, table references, syntax)
- ✅ Financial domain relevance verified for all included databases
Applications
This dataset is specifically designed for:
Financial Research Applications
- Financial Text-to-SQL Systems: Train models specifically for financial database querying
- Domain Adaptation Studies: Research cross-domain transfer from general to financial SQL
- Financial Schema Understanding: Develop models that understand complex financial relationships
- Regulatory Compliance: Build systems for automated financial reporting and compliance checking
- Risk Analysis Automation: Create tools for automated risk assessment query generation
Industry Applications
- Financial Analytics Platforms: Natural language interfaces for financial data analysis
- Banking Query Systems: Customer service and internal analyst tools
- Investment Research: Automated portfolio analysis and market research
- Regulatory Reporting: Compliance and audit report generation
- Insurance Processing: Claims analysis and policy management systems
Educational Applications
- Financial SQL Training: Teach SQL with realistic financial datasets
- Business Intelligence Education: Train on real-world financial database structures
- Fintech Development: Build and test financial technology applications
FINCH Evaluation Metric
The dataset introduces the FINCH Score, a specialized evaluation metric for financial Text-to-SQL that addresses limitations of traditional exact-match and execution accuracy metrics:
Key Features of FINCH Score
- Component-wise Scoring: Weighted evaluation of SQL clauses (SELECT, WHERE, JOIN, etc.)
- Financial Clause Priority: Higher weights for business-critical clauses (WHERE, JOIN, GROUP BY)
- Execution Tolerance: Materiality-aware tolerance for floating-point differences
- Structural Fidelity: Emphasis on semantic correctness over syntactic matching
Mathematical Formulation
FINCH Score = S(q̂,q*)^β × (δ + (1-δ)e(q̂,q*))
Where:
- S(q̂,q*): Weighted component similarity score
- e(q̂,q*): Execution accuracy with tolerance τ
- β: Structural fidelity parameter
- δ: Execution failure penalty parameter
Benchmark Results
Initial benchmarking on FINCH reveals detailed performance across multiple state-of-the-art models:
Model Performance Table
| Model | Exact Match | Execution Accuracy | Component Match | FINCH Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-OSS-120B | 1.8% | 27.8% | 16.6% | 11.6% |
| Arctic-Text2SQL-R1-7B | 0.6% | 2.3% | 3.7% | 1.5% |
| Qwen3-235B-A22B | 0.7% | 2.5% | 2.8% | 1.2% |
| Qwen3-8B | 0.5% | 0.8% | 3.5% | 1.2% |
| GPT-OSS-20B | 0.3% | 7.5% | 5.2% | 3.0% |
| Phi-4-mini-reasoning | 0.0% | 0.2% | 1.0% | 0.4% |
SQL Clause-Level Performance
Analysis of errors by SQL clause reveals systematic challenges:
| Model | SELECT | FROM | WHERE | GROUP BY | HAVING | ORDER BY | LIMIT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-OSS-120B | 4.7% | 27.3% | 6.9% | 7.5% | 6.3% | 6.3% | 73.8% |
| Arctic-Text2SQL-R1-7B | 2.5% | 3.6% | 0.7% | 4.7% | 1.0% | 1.3% | 42.7% |
| GPT-OSS-20B | 1.4% | 6.2% | 1.5% | 8.4% | 3.7% | 1.5% | 65.2% |
Model Performance Hierarchy
- GPT-OSS-120B: Strongest overall performance (11.6% FINCH Score)
- Arctic-Text2SQL-R1-7B: Best domain-adapted model despite smaller size (1.5% FINCH Score)
- GPT-OSS-20B: Solid medium-scale performance (3.0% FINCH Score)
Key Research Findings
- Domain adaptation outperforms scale alone - Arctic-Text2SQL-R1-7B (7B params) rivals much larger models
- Schema-sensitive clauses (SELECT, FROM, WHERE) remain the primary bottleneck
- Query difficulty shows steep performance degradation: easy queries achieve ~26.5% vs hard queries at ~4.5%
- Financial complexity significantly impacts all models, with even SOTA systems achieving modest absolute performance
- FINCH Score correlation: Provides more nuanced assessment than traditional exact-match metrics
Data Source & Methodology
FINCH consolidates financial databases from multiple sources:
- Careful Domain Selection: Only financial-relevant databases retained
- Comprehensive Validation: All SQL queries tested for execution
- Error Correction: Systematic fixing of syntax and schema errors
- Difficulty Annotation: Query complexity labeled following established guidelines
- Schema Normalization: All databases converted to SQLite for consistency
The curation process prioritized financial domain relevance while maintaining the diversity and complexity necessary for robust model evaluation.
Ethical Considerations
- Public Domain Data: All source databases are from publicly available benchmarks
- Financial Privacy: No real customer or proprietary financial data included
- Synthetic Data: Financial amounts and transactions are synthetic or anonymized
- Research Purpose: Intended primarily for academic and research applications
- Domain Compliance: Respects financial data handling best practices
Citation
If you use the FINCH dataset in your research, please cite:
@inproceedings{singh2025finch,
title={FINCH: Financial Intelligence using Natural language for Contextualized SQL Handling},
author={Singh, Avinash Kumar and Sarmah, Bhaskarjit and Pasquali, Stefano},
booktitle={Proceedings of Advances in Financial AI: Innovations, Risk, and Responsibility in the Era of LLMs (CIKM 2025)},
year={2025},
organization={ACM}
}
Dataset Card Contact
For questions about the FINCH dataset, please contact the research team at Domyn.
Research Team:
- Avinash Kumar Singh ([email protected])
- Bhaskarjit Sarmah ([email protected])
- Stefano Pasquali ([email protected])